Introduction to Autonomous Vehicles
As technology continues to evolve, one of the most exciting and potentially disruptive innovations is the advent of autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars. These vehicles promise to change how we think about transportation, safety, and even the environment. But what exactly are autonomous cars, and how do they work? Let’s explore the world of self-driving technology and what it means for the future of mobility.
What is an Autonomous Vehicle?
An autonomous vehicle is a car that can drive itself without human intervention. In other words, it can sense its environment, navigate roads, and make decisions—all without a human driver. These vehicles use advanced technologies like sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor their surroundings and navigate.
Autonomous cars promise to offer the same capabilities as human drivers—getting from point A to point B—while also eliminating many of the human errors and biases that contribute to accidents. However, the road to fully autonomous vehicles is still filled with challenges, both technological and legal.
How Do Self-Driving Cars Work?

Self-driving cars rely on several key components to function. These vehicles utilize sensors, AI algorithms, and real-time mapping to understand their environment and make decisions. Let’s break it down:
- Sensors & Cameras: These help the car detect and interpret objects, road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. Cameras provide visual data, while sensors like radar and lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) offer more precise data, especially in low-visibility conditions.
- AI & Machine Learning: AI algorithms process all of the sensory information and make decisions based on real-time data. These decisions range from navigation to obstacle avoidance to adhering to traffic rules.
- Mapping: Autonomous cars create a real-time map of their environment, which is constantly updated to improve navigation. This map includes everything from lane markings to traffic lights to road hazards.
The Technology Behind Self-Driving Cars
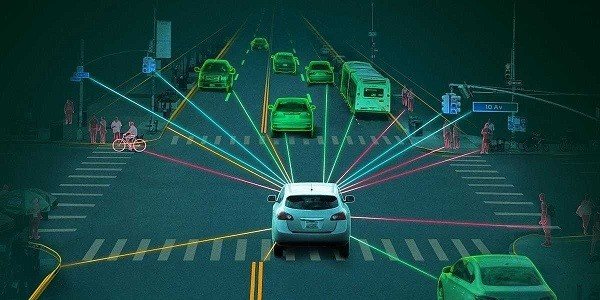
To function as a fully autonomous vehicle, self-driving cars need several sophisticated technologies working together. These include AI software for decision-making, sensors for real-time perception of the environment, and advanced actuators that control the vehicle’s steering, brakes, and acceleration.
At the heart of the system, machine learning helps the vehicle “learn” from data gathered during its journeys. Over time, it improves its ability to recognize patterns and make better decisions, effectively making the car smarter with each drive.
Sensors, AI, and Mapping: How It All Comes Together
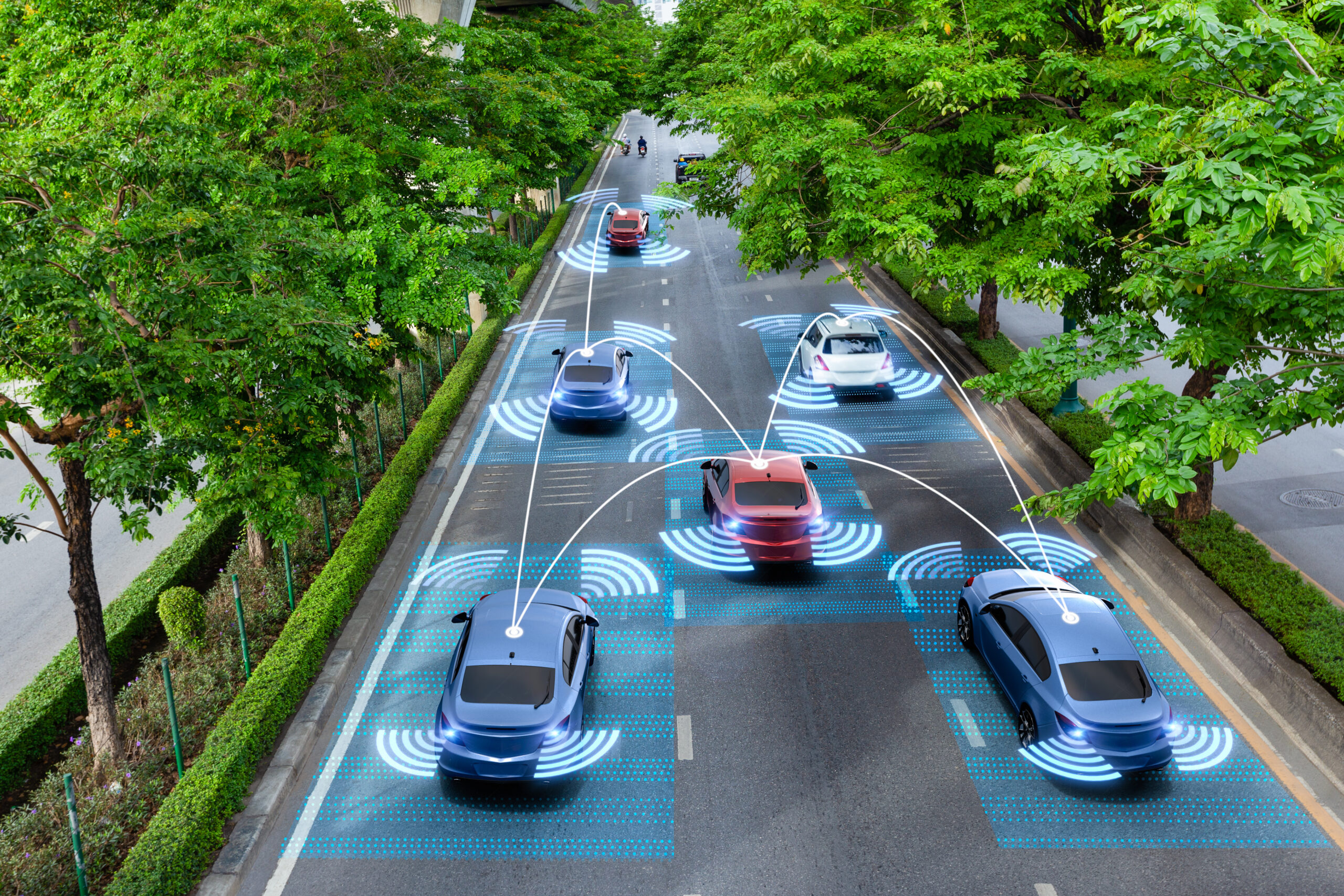
The integration of these three core technologies is what allows autonomous cars to operate smoothly. Sensors feed data into the car’s AI system, which processes the information to build a map of the surroundings. This dynamic map then helps the car make split-second decisions, like when to turn, stop, or accelerate. Additionally, AI enables the car to predict potential hazards (e.g., pedestrians, cyclists, or other vehicles) and avoid collisions.
Levels of Autonomy: What Do They Really Mean?
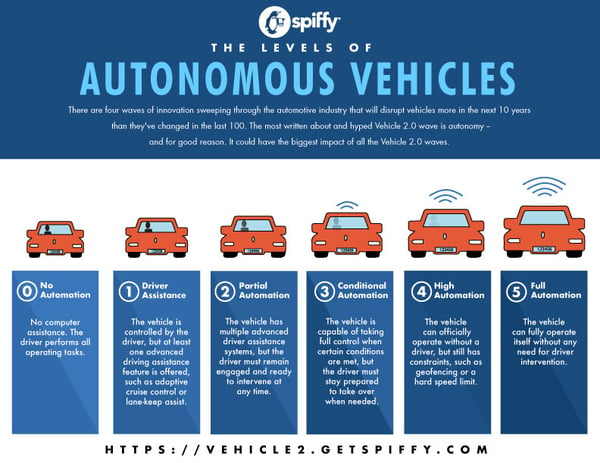
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of driving automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (fully autonomous). Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Level 0: No automation. The human driver controls the vehicle entirely.
- Level 1: Driver Assistance. Features like cruise control or lane-keeping assistance.
- Level 2: Partial Automation. The car can control speed and steering, but the driver must remain engaged.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation. The car can drive itself under certain conditions, but the driver must be ready to take control.
- Level 4: High Automation. The car can drive itself within certain conditions or locations (e.g., geofencing) without needing a driver.
- Level 5: Full Automation. No human driver is required, and the car can operate anywhere, under any condition.
Autonomous vs. Automated: Understanding the Difference
What’s the Difference Between Autonomous, Automated, and Self-Driving?
The terms “autonomous,” “automated,” and “self-driving” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. “Autonomous” refers to a vehicle that requires no human input at all (Level 5). “Automated” generally refers to a vehicle with automated systems that assist the driver (Levels 1-4), while “self-driving” typically refers to cars that can drive themselves but still need a human backup (Level 3 and 4).
Autonomous vehicles are the future of transportation, offering benefits like safety, convenience, and environmental sustainability. While there are many hurdles to overcome, the potential rewards are immense. The road ahead is still under construction, but we’re getting closer to a world where self-driving cars are a common sight on the roads.


